
Most Important Electricity Numericals Electricity Class 10 Numericals Class 10 Science (LIVE
Frequency of appearance: ★ ★ ★ ★ ★. Q2. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. ( i ) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. ( ii ) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 − 19 C , then calculate the total number of electrons flowing.
Top 10 Electricity Numericals Class 10 Electricity Class 10 Notes Class 10 Science Chapter
Question 18: (a) State the relation between potential difference, work done and charge moved. (b) Calculate the work done in moving a charge of 4 coulombs from a point at 220 volts to another point at 230 volts. Solution : (a) Potential difference = Work done/Charge moved. or Work done= Potential difference x Charge moved (b) V1=220 V, V2=230V, Charge moved=Q=4C Thus, the potential difference.

ncert solutions for class 10 science chapter 12 electricity saq 5s 2 ncertsolutions cbse
Get NCERT Solutions, Notes, Numericals (with solutions) of Chapter 12 Class 10 NCERT Science- Electricity. It is a Physics Chapter, from which numericals always come in Board Exams.. At Teachoo, in addition to solving all the NCERT Back Exercise Questions. we have also solved Questions which are given in boxes between the chapter, Examples from the chapter, as well as Notes.

Electricity Class 10 Ncert Questions With Answers Part 2 Physics Youtube Photos
Electric charge is conserved, additive and quantised. The S.I. unit of electric charge is 'C' coulomb. Any other charged body will have a charge Q Q = ne where n is the number of electrons and e is the charge on electron = 1.6 x 10-19 coulombs. Electric current Electric current is a flow of electrons in a conductor such as a metal wire.

Physics Class 10th Current Amp Electricity Part 1 Youtube
Important Questions of Electricity Class 10 Science Chapter 12. Question 1. A current of 10 A flows through a conductor for two minutes. (i) Calculate the amount of charge passed through any area of cross section of the conductor. (ii) If the charge of an electron is 1.6 × 10 -19 C, then calculate the total number of electrons flowing.

Electricity Numericals very important Science chapter 12 class 10 /numericals of
NUMERICALS Electricity & its effects 2. Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge per second through any cross section of a conductor. 3. How much work is done in moving a charge of 2 C across two points having a potential difference of 12 V ? 4. How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V

Class 10 Electricity Numericals / Problems Learn to solve any Numericals on Electricity Part1
Given below are all the formulas used for class 10 electricity chapter. Charge q on a body is always denoted by. q = ne q = n e. where n = any integer positive or negative and e = 1.602×10−19C e = 1.602 × 10 − 19 C i. e., charge on an electron or proton. W ork done =charge ×potential W o r k d o n e = c h a r g e × p o t e n t i a l or.

Practice Problems for Electricity Class 10 Teachoo Science
Numericals for Electricity Class 10. Numericals for Electricity in Class 10 are an integral part of the curriculum, aimed at developing a deeper understanding of electrical concepts. These numerical problems involve practical applications of Ohm's law, resistivity, electric power, and other electrical parameters.

MOST IMPORTANT ELECTRICITY NUMERICALS CLASS 10 CBSE & ICSEIn One Shot YouTube
Answer. In an electrical circuit two resistors of 2 Ω and 4 Ω respectively are connected in parallel to a 6 V battery. The heat dissipated by the 4 Ω resistor in 5 s will be. (a) 45 J. (b) 20 J. (c) 60 J. (d) 35 J. Answer. A cell, a resistor, a key and ammeter are arranged as shown in the circuit diagrams below.
Electricity Numericals Class 10 Science Term 2 Exam 🔥 All types of Questions Covered 👍 YouTube
Activity 12.1. Set up a circuit as shown in Fig. 12.2, consisting of a nichrome wire XY of length, say 0.5 m, an ammeter, a voltmeter and four cells of 1.5 V each. (Nichrome is an alloy of nickel, chromium, manganese, and iron metals.) First use only one cell as the source in the circuit.

gave me some numericals from ch 1 electricity (physics) class 10 for exam cbse Brainly.in
Solved Electricity numerical for class 10 1. Question: Two bulbs have ratings 100 W, 220 V and 60 W, 220 V respectively. Which one has a greater resistance? Answer: P=VI= V2/R For the same V, R is inversely proportional to P. Therefore, the bulb 60 W, 220 V has a greater resistance. 2. Question: A torch bulb has a resistance of 1 Ω when cold.

Electricity Numericals Class 10, Part 04 YouTube
Document Description: Previous Year Questions: Electricity for Class 10 2024 is part of Science Class 10 preparation. The notes and questions for Previous Year Questions: Electricity have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Previous Year Questions: Electricity covers topics like Short Answer Type Question, Long Answer Type Questions and Previous Year.
️Electricity Physics Worksheet Free Download Gmbar.co
Prepare for class 10 CBSE exam for the chapter Electricity by revising difficult board-type numerical questions. Created by Mahesh Shenoy. Questions.

Selina Solutions Concise Physics Class 10 Chapter 8 Current Electricity Get PDF Here
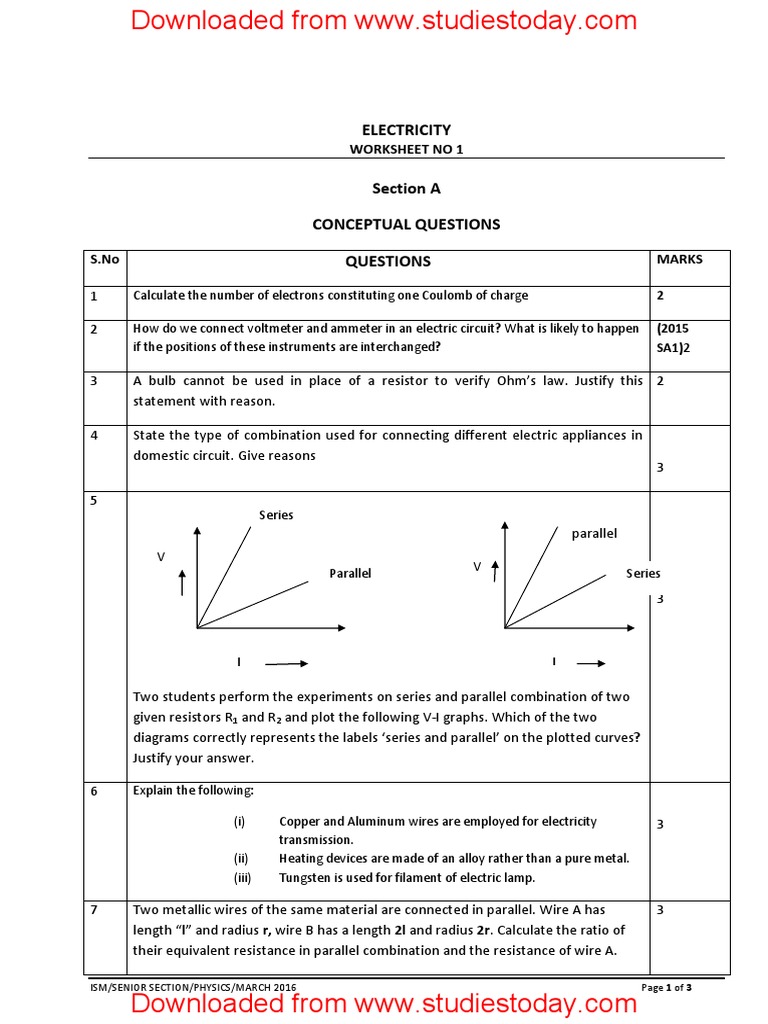
Worksheets play an important role in developing an understanding of Chapter 12 Electricity in CBSE Class 10. Students can download and save or print all the worksheets, printable assignments, and practice sheets of the above chapter in Class 10 Science in Pdf format from studiestoday.

Electricity Numericals Class 10 CBSE YouTube
These numericals on electricity are important and are always asked in the Class 10 CBSE, RBSE, and other board examinations. Numerical Problems based on Ohm's law To solve the numericals on electricity based on Ohm's law , we will use the following formulas

Selina Solutions Concise Physics Class 10 Chapter 8 Current Electricity Get PDF Here
This post presents a few important numerical problems in physics that you can solve using the concepts of resistivity. If you want a quick revision to memorize the resistivity formula then you can check this post on resistivity formula derivation.. Note: Remember that: (1) resistivity is a property of the material (2) the unit of resistivity is ohms times metres and not ohms per metre.